(12) Tips when you use a coil | Tips for COIL users(Part-1)
(12) Tips when you use a coil
The last twelfth topic is about "Tips when you use a coil".
For better understanding of coil performance
Although a coil and a capacitor are same electronic component, there may be more difficulty to understand coil, comparing with capacitor. It may be because the capacitor is a voltage element while the coil is a current element.
It is generally known that "It can be used if the electronic device has the same operation voltage". Therefore, even ordinary people know that "a product with AC 100V cannot be used at AC 200V".
So, which phrase do you think is easier to understand, (1) or (2)?
- When applying voltage to a resistor, a current flows in the resistor.
Voltage → Current - When a current passes through a resistor, a voltage occurs at both ends of resistor.
Current→ Voltage
Probably, most of people think it is easier to understand (1). The coil and the capacitor are in an electrically-opposing relationship. So, when you think an performance of coil (current), it may help you when it is compared with capacitor(voltage). Let us see the contents which are paired in Table-1.
| Capacitor | Inductor |
|---|---|
| Voltage | Current |
| Voltage source |
Current source |
| Parallel | Series |
| Series | Parallel |
| Open | Short |
| Short | Open |
| E = 0 | I = 0 |
| I = ∞ | E = ∞ |
When we explain with figures, SW is turned on in the connection diagram on the left of Figure-1, and a voltage is applied between terminals of capacitor. Then SW is turned off so that it is charged.
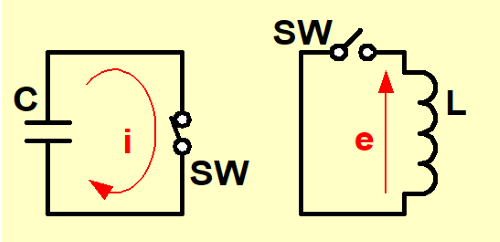
After that terminals are contacted (SW is closed), a big current (i) flows for a moment as shown in Figure-2 (The spark tells you that the electrical energy was generated).
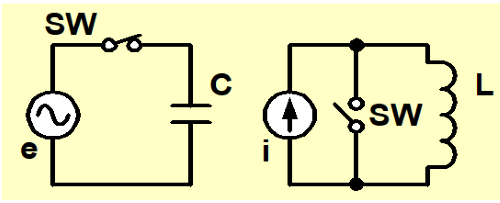
In the same way, SW is turned off in the connection diagram on the right of Figure-1, and a current is supplied to the coil. Then SW is closed like a loop with keeping the current flowing. After that the power is separated.
Then, when the circuit is opened (SW is opened), a big voltage (e) is generated for a moment as shown in a Figure-2. Actual discharge event shows that the electrical energy is generated.
I hope that in this way, it could be understood that the coil and the capacitor are same if we think from a different aspect,…yet you may still think it is easier to understand the voltage!
The generation of back electromotive force
As explained above, if a current is interrupted for a moment by a switch or a transistor during supplying current through a coil, very high voltage is generated on the both ends of coil to try to keep supplying the current through the coil.
There is a way to generate a high voltage by using this phenomenon. However, in the case of the circuit which current through coil is ON-OFF, other studies will be necessary such as a protection circuit for high voltage.
Attention must be paid in the case like putting a choke coil in a power supply for noise control during prototype study as the similar situation may happen.
Frequency characteristics
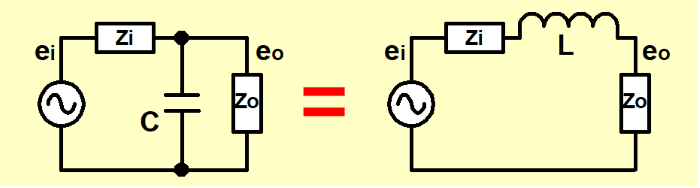
For both coil and capacitor, their impedance and electrical characteristics change depending on frequency. If we think the frequency characteristic of coil in a circuit in a contrast with capacitor, based on Table-1 following circuits show similar frequency characteristics (refer to Figure-3): "Capacitor put on a circuit in series(parallel)"="Coil put on a circuit in parallel(serial)" However, it must be considered that the fundamental operation is different.
Failure mode of coil
For wire wound coil, there are various causes of failures, and the most major failure mode is "disconnection (open circuit)".Besides, when a coil is used under bad condition, short circuit may occur between wires due to insulation degradation of wire coating.
In the case of the disconnection, a coil becomes open, and a current is interrupted. The damage is smaller than the one becoming short circuit in the most cases, however the disconnection may have a great impact to other components.
In mechanical failure, there is a cause "removed solder section between a coil terminal and circuit board ", which occurs in the case like vibration is applied continuously.
If a device which our coil is put requires high reliability and safety against failure, attention must be paid to such failure modes as well as selecting the coil which reliability was fully studied.
Photo-1 & -2(Photo-2 shows bottom side of product)show our CWD・CWR series developed for automotive application. These have 4 terminals structure to ensure high resistance to impact and vibration.

※CWR1277C,CWD1242C This product is not currently in the lineup.
If impact is made to coil
It often happens that a component is dropped to a floor accidentally, and the impact is made to it. If a floor is hard like a concrete, the impact reaches 1,000G although it is short time (several mill seconds).
Ferrite core is used for many of coil as magnetic materials. If big impact is made, it may be damaged same as ceramics (china).
We think that nobody uses the coil which dropped and damaged on the appearance. Even if there is no damage in an appearance, the inside of a ferrite core may have cracked with the impact. We strongly recommended not using the dropped coil.
In closing
We could complete total 12 topics of the first series. We appreciate that a lot of people have read them than expected. Thank you very much. We hope it will be useful for your work as much as possible.

Author
Yasuo Hoshino
born in1954, is a prominent coil specialist at SAGAMI ELEC CO., LTD.
He joined Sagami Musen Works, a former company of SAGAMI ELEC, in 1976 and has been working in the engineering department for over 40 years.
During his career at Sagami, he has served as a technical manager and a member in board.
He supported the firm as an technical advisor and retired at the end of March 2024.His technical advice helped many engineers.
Photography is his life's work. His favorite animals are cats and cricket.
- Some of the products listed in this document are no longer in production.
- As some time has passed since the article was written, the information provided may still contain outdated content.
If you have anything, you can send e-mail by clicking here.
Tips for COIL users Part-1
- (1) Differences between Coil and Inductor
- (2) Main parameters of the inductor
- (3) Inductance of the coil parameters
- (4) Temperature rising of inductor
- (5) What's Q
- (6) Self Resonance Frequency of Inductor
- (7) Open and close magnetic circuitr
- (8) Eddy current & Shield
- (9) Temperature and insulation characteristics
- (10) Operation of coil
- (11) Coupling of coil
- (12) Tips when you use a coil
