(9) Temperature and insulation characteristics | Tips for COIL users(Part-1)
(9) Temperature and insulation characteristics
The ninth topic is about "temperature characteristic and insulation characteristic" that are the rest of characteristics.
Temperature characteristic of inductance
Most of coils are made by using magnetic materials. As the result, the coil characteristics vary depending on magnetic materials and a coil structure (magnetic structure).
For ferrite cores which are used as the magnetic materials, most of permeability (μi) have the positive temperature characteristic. Therefore, in general the temperature characteristic of inductance is also positive (if the temperature rises, the inductance increases). However, even though same materials are used for a coil, if the structure is different, the temperature characteristic may significantly vary.
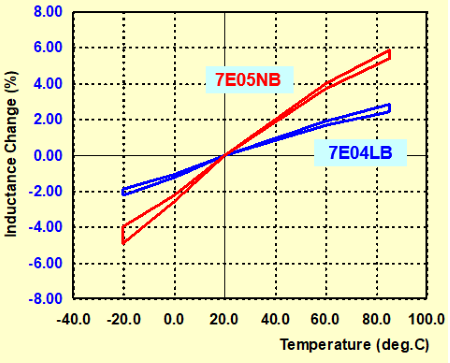
Graph-1 shows an example of temperature characteristic of 7E04LB and 7E05NB, our power inductors. Two coils have almost the same structure, but there is a difference in the temperature characteristic because the ferrite core materials are different.
When we develop the power inductors, we put more value on the DC saturation current than the temperature characteristic of inductance. Therefore, such difference may appear.
Although the appearances are similar, the characteristics are not always same. Therefore, please confirm the temperature characteristic as required.
※7E05NB This product is not currently in the lineup.
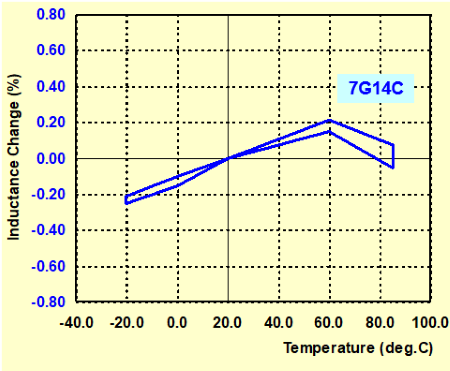
Graph-2 shows an example of temperature characteristic of our inductor 7G14C for digital amplifier. Please note that the scale (blue) of vertical axis is ten times different between Graph-1 and Graph -2.
All 7E04LB, 7E05NB and 7G14C are shielded inductors, but you can find that "variation for inductance temperature" is significantly different due to the structure difference.
It is not that the temperature characteristic is set as large value intentionally.
Temperature characteristic of DC saturation allowable current
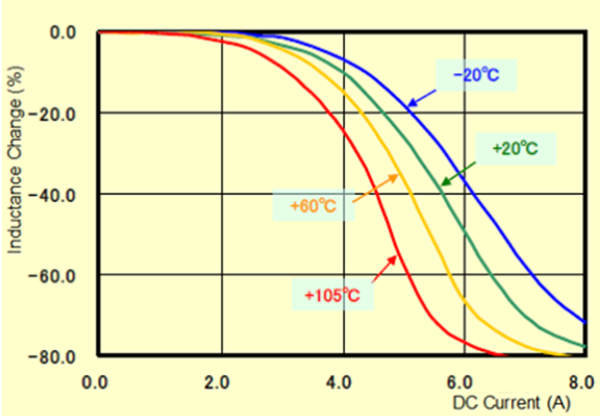
When the temperature rises, generally a curve of DC saturation current of power inductor comes to the left side like Graph-3 (characteristic example of our CER1042B). Although the level varies depending on the structure and the ferrite core materials which are used, it tends to be like the one in Graph-3.
For the power inductors, it is important to confirm the variation of characteristics based on high temperature, because the power inductors generate heat by themselves when the current is supplied, and they are mostly used at the place where the temperature relatively rises.
Insulation resistance
There are two kinds of ferrite cores which are used for coils: nickel series (Ni-Zn) and manganese series (Mn-Zn). Outstanding difference except magnetic characteristic is volume resistivity. The nickel series is 1000000Ω・m and the manganese series is 0.1 to 10Ω・m. The metal is around 0.000000001Ω・m.
It is difficult to understand, so we tried measuring the surface of ferrite core of manganese series. And when "the gap of probes was 5mm", the value was around 150kΩ.
For the nickel series, it is acceptable to consider the ferrite core as the insulation. For the manganese series, the ferrite core is available in the range of general voltage. However, some measures are necessary in the high-voltage circuit, or the circuit for which the insulation is important.
Therefore, for the manganese, the surface of ferrite core is insulated to maintain the characteristics equivalent to the nickel series depending on the application (It is employed for our power inductor series HER).
Generally, the nickel series is used for the power inductors, and the manganese series is used for the transformers. However, the (insulated) manganese series is used for some power inductors to improve DC saturation allowable current.

Author
Yasuo Hoshino
born in1954, is a prominent coil specialist at SAGAMI ELEC CO., LTD.
He joined Sagami Musen Works, a former company of SAGAMI ELEC, in 1976 and has been working in the engineering department for over 40 years.
During his career at Sagami, he has served as a technical manager and a member in board.
He supported the firm as an technical advisor and retired at the end of March 2024.His technical advice helped many engineers.
Photography is his life's work. His favorite animals are cats and cricket.
- Some of the products listed in this document are no longer in production.
- As some time has passed since the article was written, the information provided may still contain outdated content.
If you have anything, you can send e-mail by clicking here.
Tips for COIL users Part-1
- (1) Differences between Coil and Inductor
- (2) Main parameters of the inductor
- (3) Inductance of the coil parameters
- (4) Temperature rising of inductor
- (5) What's Q
- (6) Self Resonance Frequency of Inductor
- (7) Open and close magnetic circuitr
- (8) Eddy current & Shield
- (9) Temperature and insulation characteristics
- (10) Operation of coil
- (11) Coupling of coil
- (12) Tips when you use a coil